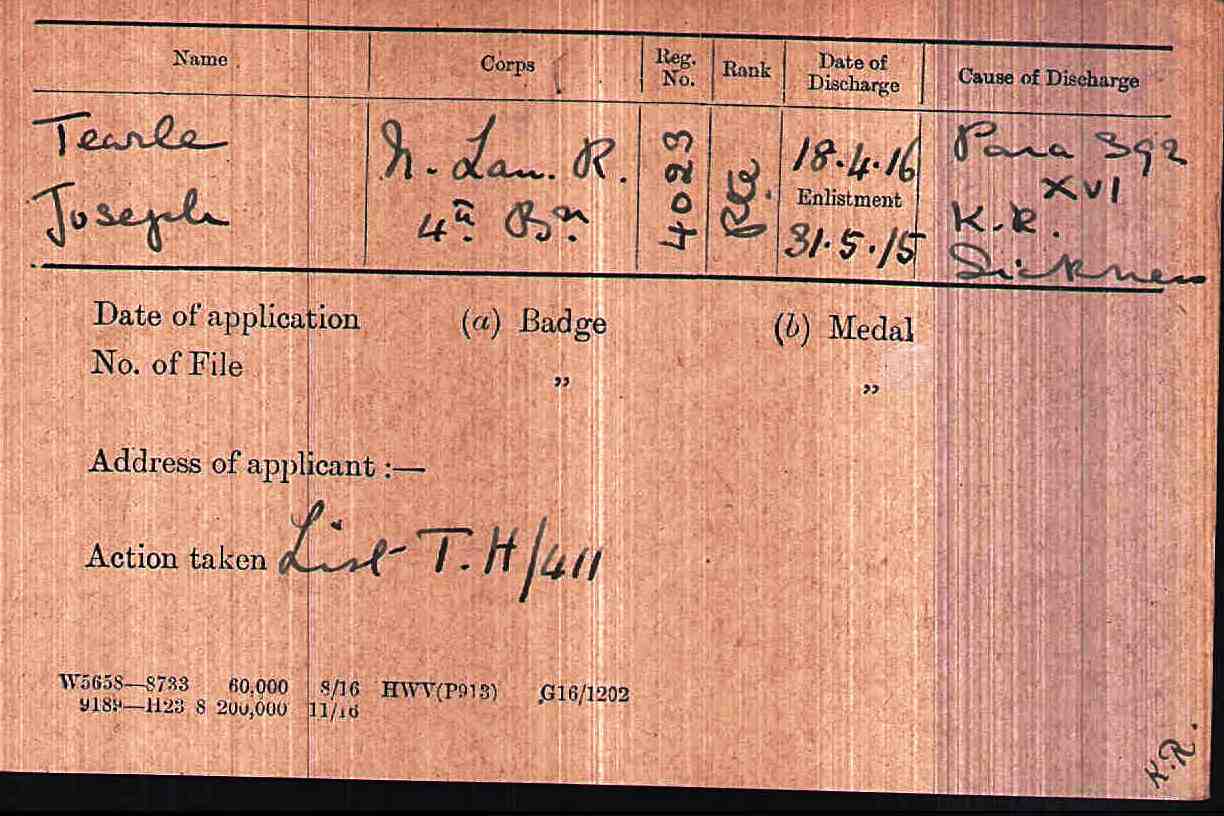
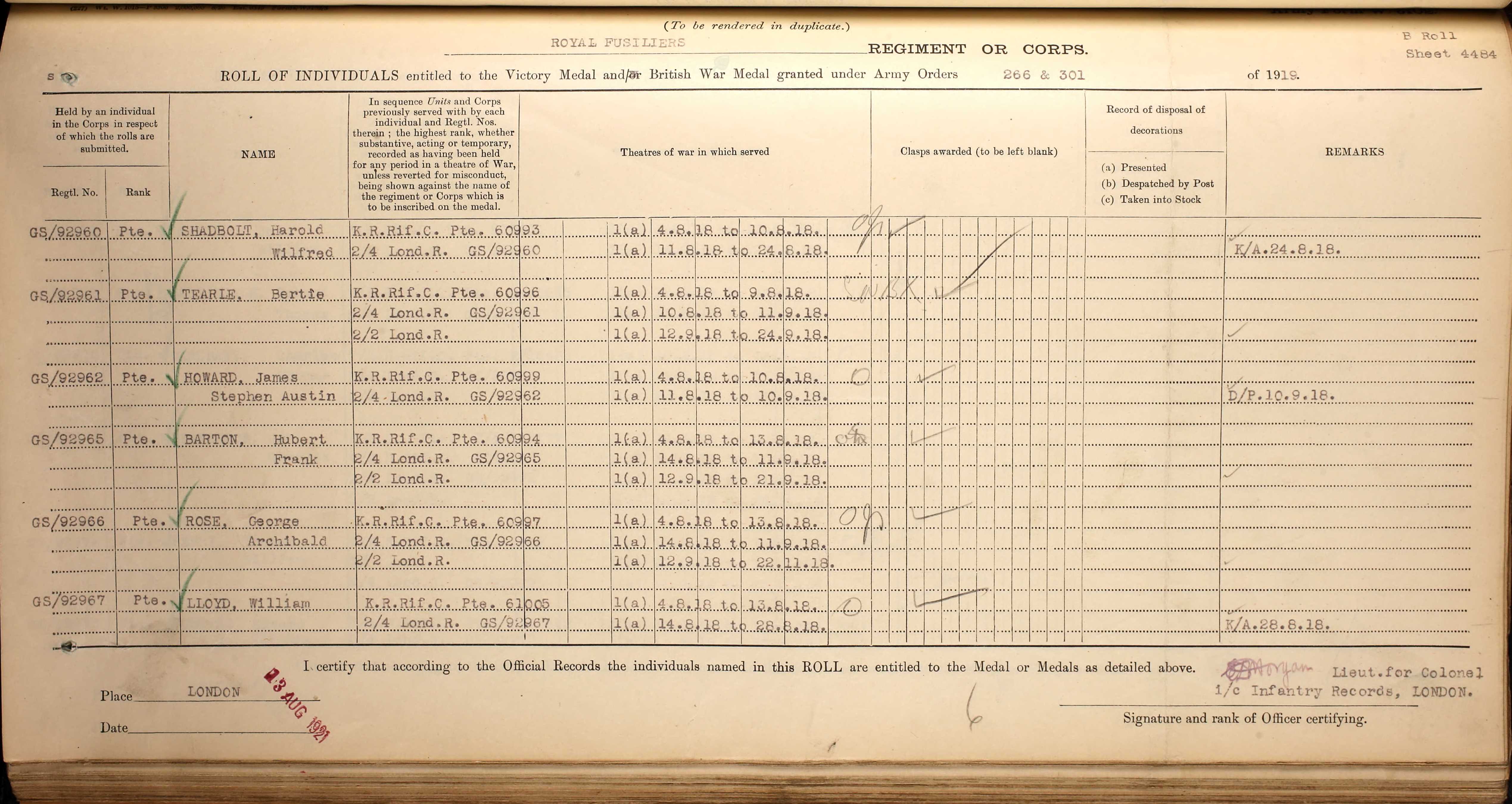
Charles E W & son Charles F S Tearle
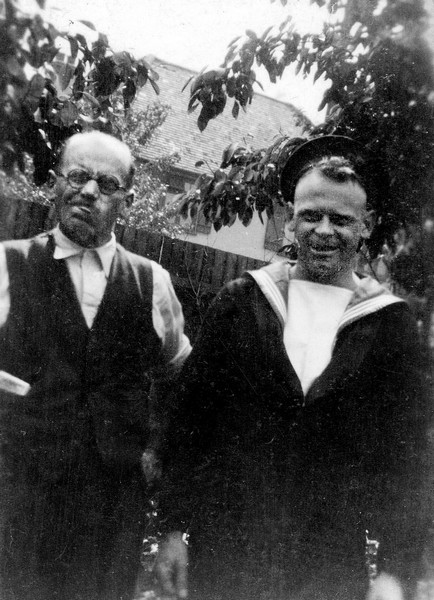
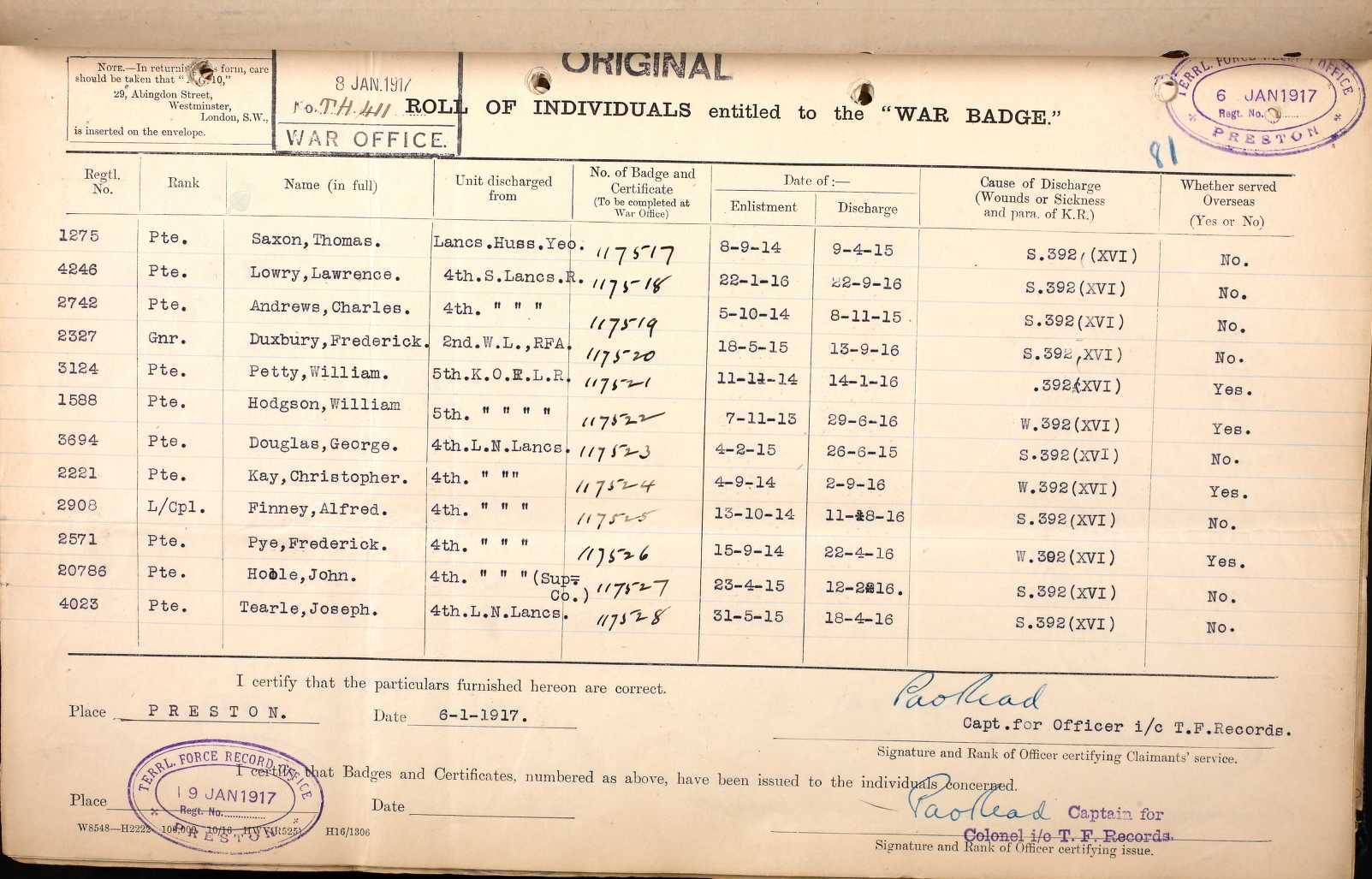
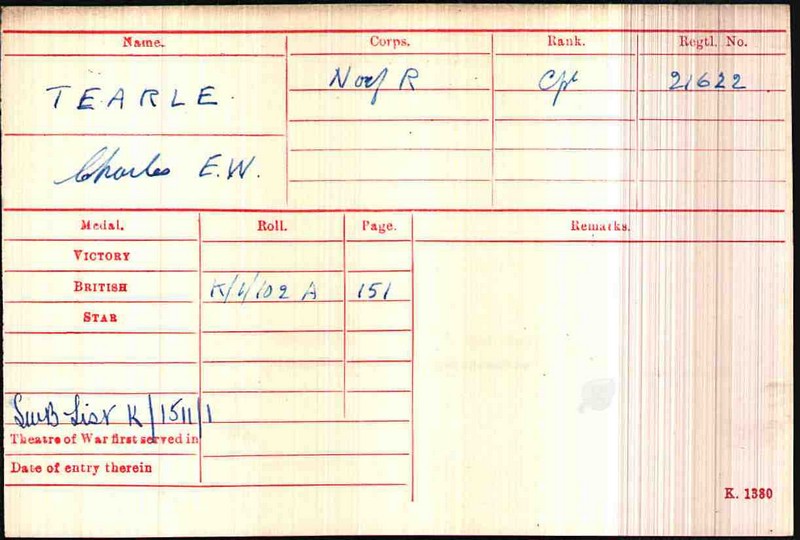
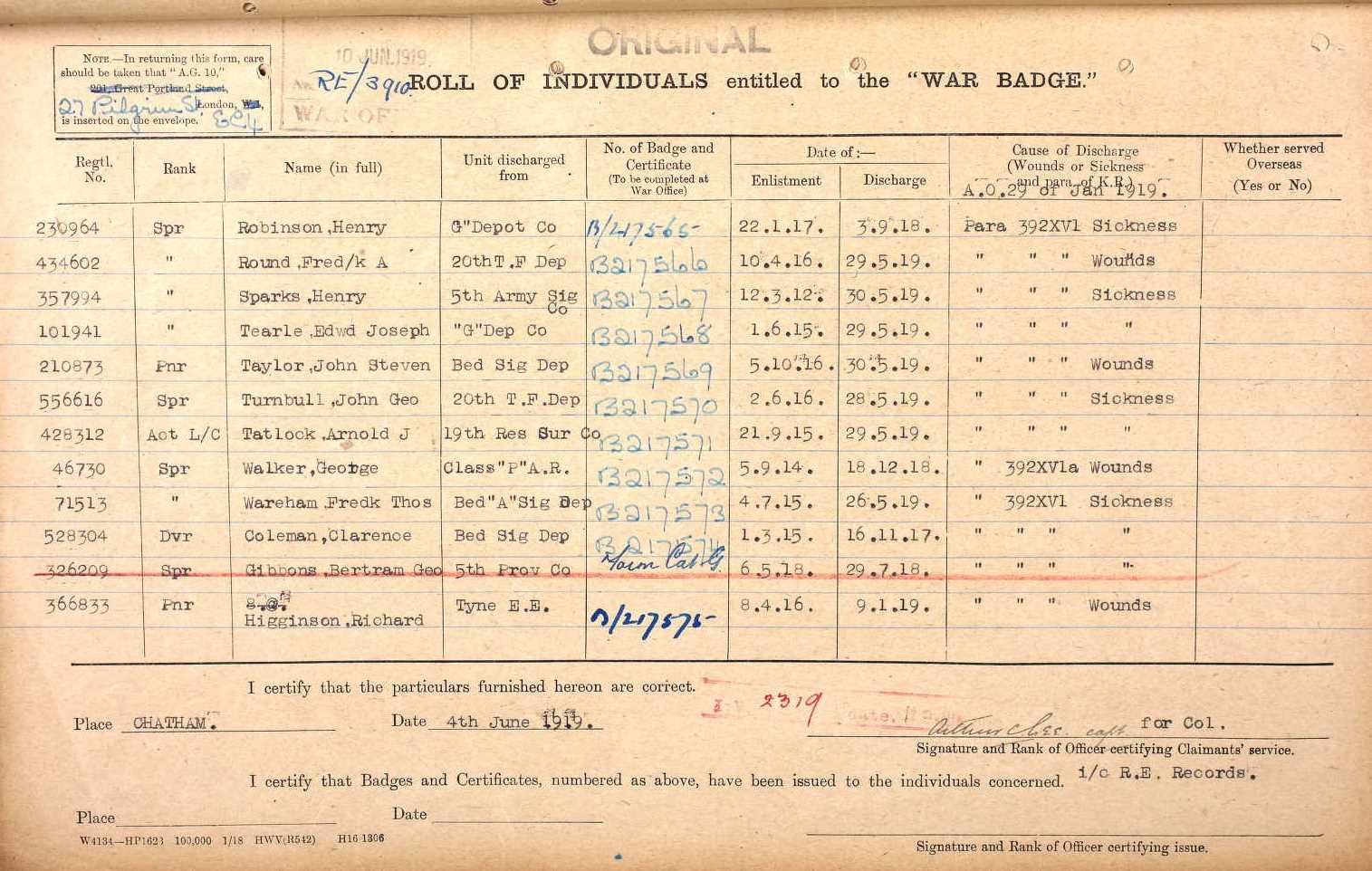
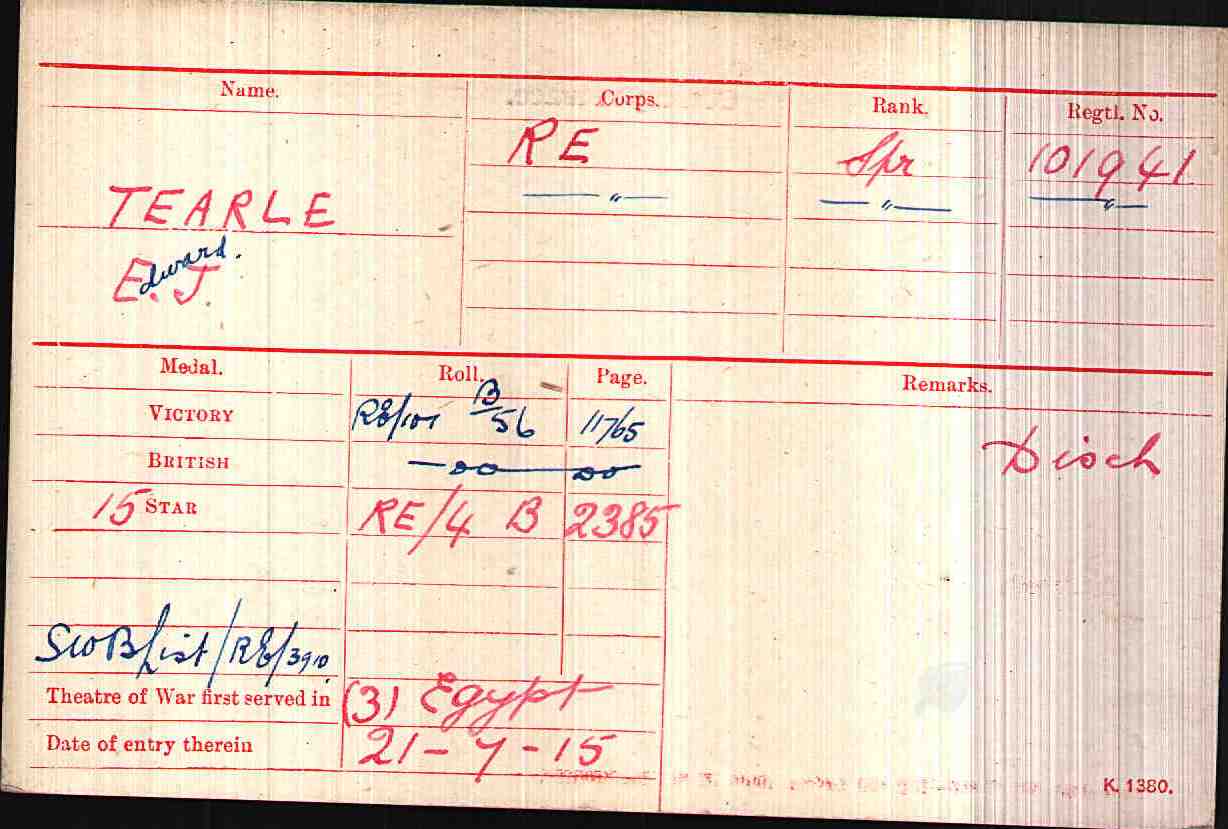
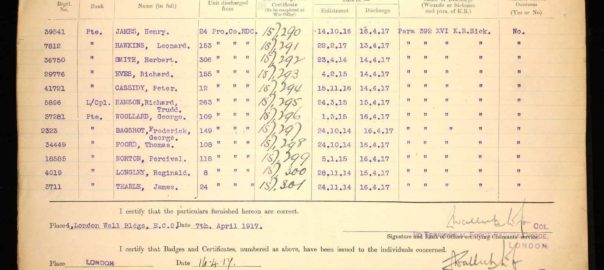
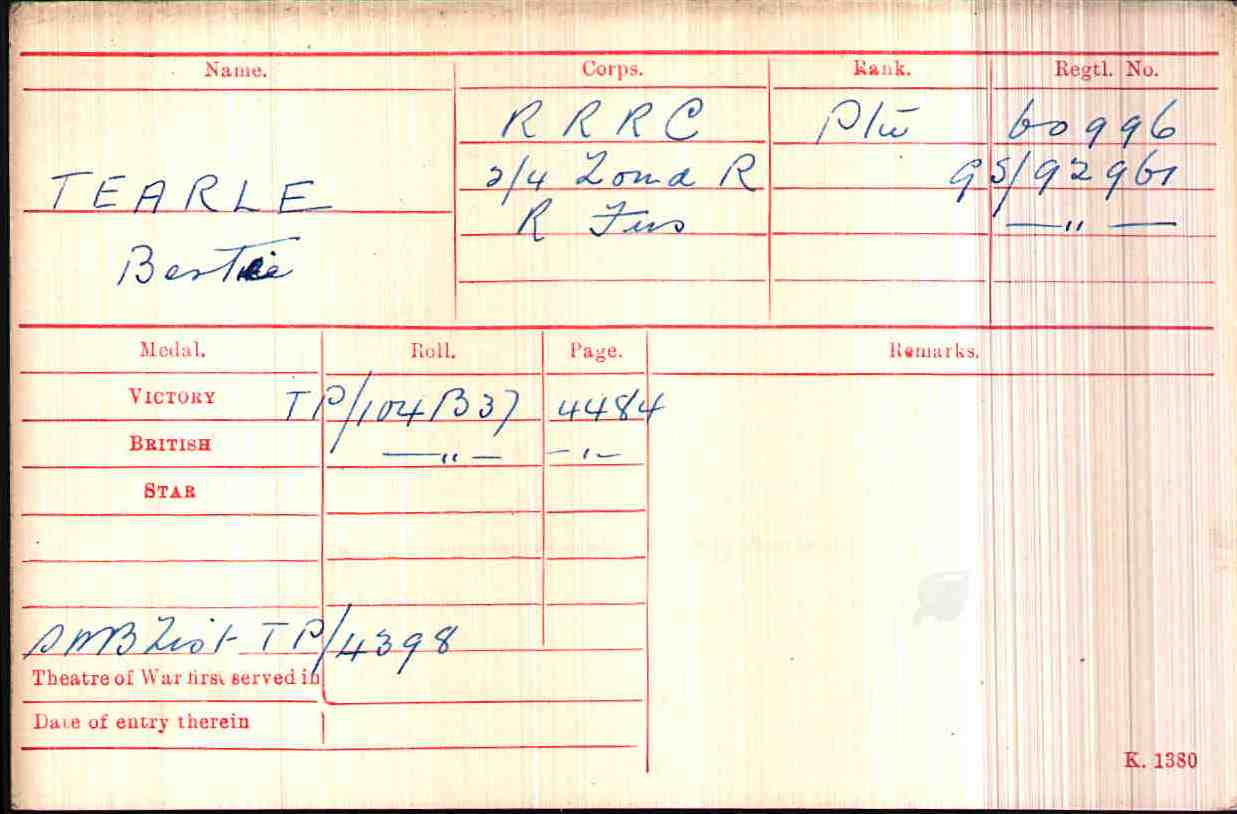
Charles Francis Stewart Tearle 1912, of Edmonton, Essex was the son of Charles Ernest Walter Tearle 1863, of Southwark, London, who fought with the Norfolk Regiment in WW1 and was awarded the Silver War Badge because of the severity of a sickness he caught on active duty. If you look up the reference above you will be able to see the ancestry details of Charles 1912, who is on the branch of Joseph 1737.
In the photograph the two men, Charles E W on the left and Charles 1912, are having a lark with the photographer (Mrs Tearle?) As you can see Charles Jnr is in full navy uniform. Here is the record of Charles 1912 from CWGC:
Name: TEARLE, CHARLES FRANCIS STEWART
Initials: C F S Nationality: United Kingdom
Rank: Able Seaman Regiment/Service: Royal Navy
Unit Text: H.M.S. Culver
Date of Death: 31/01/1942 Service No: P/JX 235706
Casualty Type: Commonwealth War Dead
Grave/Memorial Reference: Panel 65, Column 1.
Memorial: PORTSMOUTH NAVAL MEMORIAL

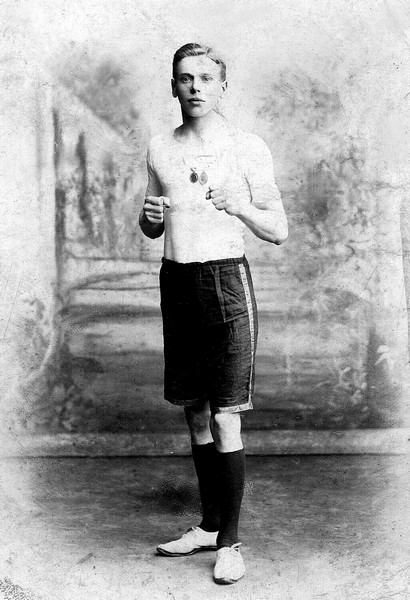
Charles Francis Stewart Tearle
The Royal Navy archives note that the Culver was American-made:
Type: Sloop
Class: Banff
Pennant: Y 87
Built by: Bethlehem Shipbuilding Corp. (Quincy, Massachusetts, U.S.A.)
Laid down: 20 Jun, 1928 Launched: 27 Nov, 1928
Commissioned: 30 Apr, 1941
Lost: 31 Jan, 1942
A short history of the ship noted the following:
Former name: USCG Mendota (It was originally built for the US Coast Guard, and you would wonder if a 1928 ship was going to cut it in a 1940s conflict.)
History: At 23.31 hours on 31 January 1942, U-125 fired a salvo of four torpedoes at the convoy SL-98 and observed two hits and a large explosion. Schuch thought that he had hit an ammunition freighter, but in fact it was HMS Culver (Lt.Cdr. R.T. Gordon-Duff, RN) that had blown up in position 48.43N, 20.14W with the loss of the commanding officer, seven officers and 118 ratings.
Hit by U-boat. Sunk on 31 Jan, 1942 by U-105 (Schuch).
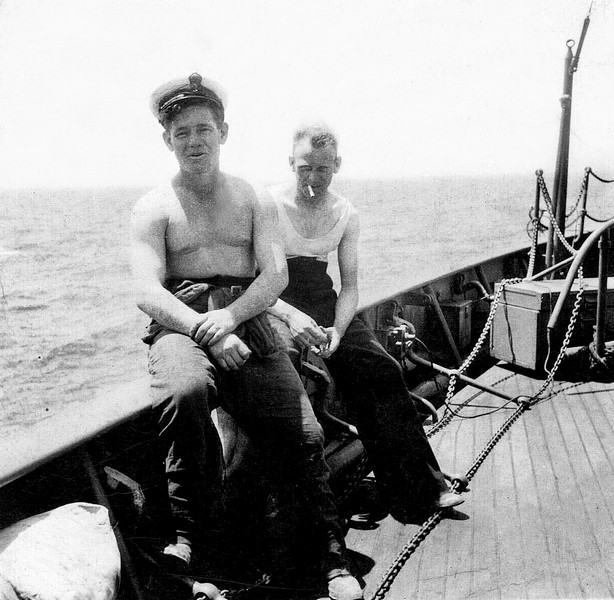

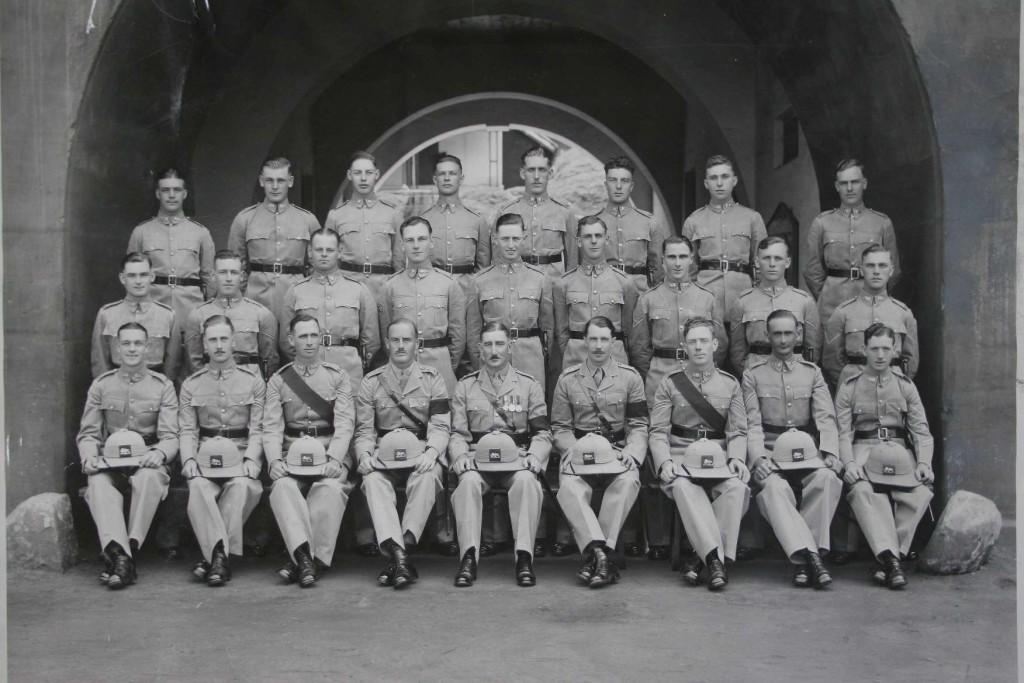
Charles F S Tearle (behind) on board the HMS Culver.
In the Royal Navy, ship’s companies seldom wore life-jackets, although they were carried aboard all vessels. Since the ship was observed to have blown up in a huge explosion, it was likely that few would have survived the first seconds of the incident, and those who did would probably not have access to a life-jacket in the short time it took for the Culver to sink.
You can see above that Charles’ permanent memorial (and the only one I know of) is his name on the Southsea Naval Memorial in Portsmouth. The Portsmouth memorial looks identical to the Plymouth memorial. Here is the obelisk:
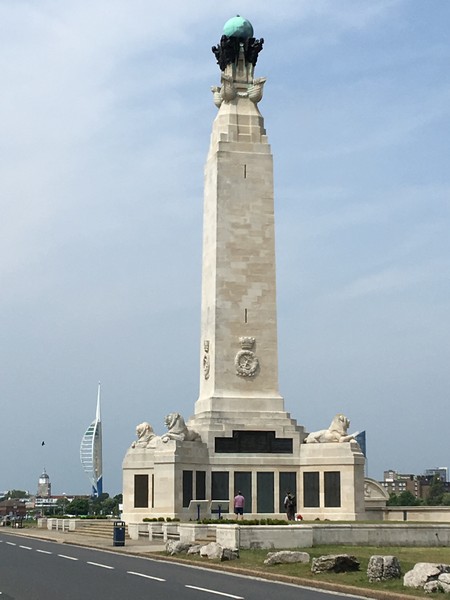

Here is Charles’ name on the Portsmouth Naval Memorial on Southsea Common on Panel 65, Column 1, just where CWGC said it was.

A Hertfordshire archive gave me a little more information on the ship:
HMS Culver was a Sloop of the Banff type, built by Bethlehem Shipbuilding Corp. (Quincy, Massachusetts, U.S.A.). She was launched on 27 November 1928. At 23.31 hours on 31 January 1942, U-105 fired a salvo of four torpedoes at the Sierra Leone convoy SL-93, west of the Bay of Biscay, and observed two hits and a large explosion. Although the U-boat thought that they had hit an ammunition freighter, they had in fact hit HMS Culver (Y 87) (Lt.Cdr. R.T. Gordon-Duff, R.N.) that blew up with the loss of the commanding officer, seven officers and 118 ratings. There were only 13 survivors.
A history of the US Coast Guard gave me some information on the Mendota:
Mendota, 1929 (later – HMS Culver, Y-87)
The cutter Mendota was named for the largest of the “Four Lakes” near Madison, Wisconsin.
Builder: Bethlehem Shipbuilding Corporation, Quincy, MA
Launched: 27 November 1928
Commissioned: 23 March 1929
Displacement: 2,075 tons
Dimensions: 250′ oa (236′ bp) x 42′ x 12′ 11″ draft (mean)
Machinery 1 turbine-driven electric motor (General Electric), 2 boilers, 3,350 shp, 14.8 knots (cruising), 17.5 knots max
Propellers: single, 4 blades
Complement: 97 (1940)
Armament: 1 x 5″/51; 1 x 3″/50; 2 x 6-pdrs (1929)
Cost: $900,000 each (hull & machinery)
“LAKE”-CLASS DESIGN
The 250-foot class cutters were designed by the Coast Guard and were, in many respects, modernized 240-footers. Captain Q.B. Newman, USCG, designed its innovative turbine-electric-drive power plant, which developed an amazing 3,350 shp. These were the first to have alternating current, and a synchronous motor for propulsion. The whole ship ran off the main turbine. The auxiliary generators were tied into the main generator electrically, after sufficient speed was attained. At that point, no steam was required to drive the turbines on the auxiliary generators. The propulsion plant achieved remarkable efficiency. The counter stern and plumb bow of the older class had given way to the flared stem and cruiser stern. These features were an attempt to improve sea qualities over the 240-foot class, particularly to eliminate the heavy shocks common in the North Atlantic Ice Patrol.
Initially this class was made up of ten cutters, all of which were transferred to Great Britain under Lend-Lease in 1941. They were to be replaced in the USCG inventory by the 255-foot Owasco-class vessels, laid down in 1943. Three vessels were lost while in British service, one was not returned, and the remainder turned back to the Coast Guard in 1946.
A 250-feet long ship is quite a sight, and in 1928, the Mendota would have been a modern and sizeable fighting vessel. As we can see above, she was used for patrolling convoys that carried goods to and from India, Africa and the US during WW2. It was simply desperate bad luck that the Culver was struck by a torpedo while on convoy duty. Of the ten cutters hired to the Royal Navy only three were lost, and sadly for us, the HMS Culver was one of them, and we lost Charles Francis Stewart Tearle along with her.
All the photographs in this story are thanks to the generosity of Paul Ailey, and my sincere thanks to him are recorded here.