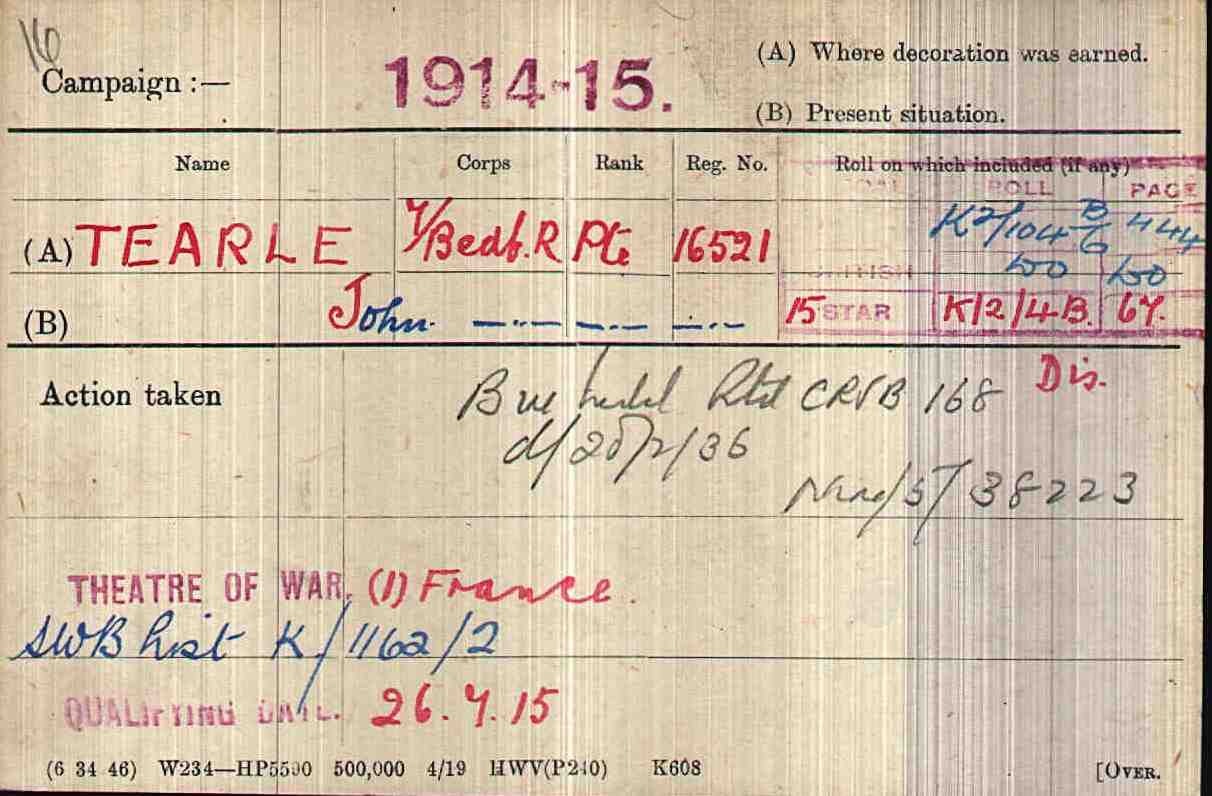
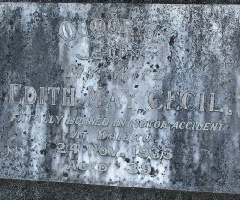A short history of Toddington Manor
The manor of Toddington dates back to the 11th century at least when its fifteen and a half hides were held by Wolfweird ‘Levet’ before the Conquest. In the 1240s it was held by Simon de Montford by virtue of his having married Eleanor, sister of Henry III whose first husband, William Marshall, Earl of Pembroke had been granted the manor following that marriage. It later passed to Roger Bigod, the King’s seneschal who, when he died in London, ordered that his body be buried there, but his heart be buried at Toddington. In 1362, the manor was worth £12 12s 8d indicating how the manor had suffered from the plague earlier that year.
In the early 15th Century, Sir Thomas Cheney of Kent married Ann Broughton, heiress of Sir John Broughton in Toddington. There was no manor house at that stage for it was their son, Henry who began the building in 1559 following the death of Sir Thomas. In 1563, Henry was knighted here by Elizabeth I. The imposing mansion, based on three courts, was three storeys high with four-storey round towers at each corner, and a 210ft-long frontage from north to south. But Sir Henry died childless in 1587 and the estates passed to his widow, Jane. She was from the Wentworth family, daughter of the 1st Baron Wentworth. Though the manor was to stay in the Wentworth family for the next few generations, it had a chequered career. King James I was entertained there in 1608 but when Jane died in 1614 the estates passed on again to her great-nephew, Sir Thomas Wentworth, the 4th Baron and later Earl of Cleveland. Unfortunately both he and his son ran up massive debts. The manor, which had been sequestered by the Commonwealth, then passed to Cleveland’s granddaughter, Henrietta Maria, Baroness Wentworth.
In 1683, her lover, The Duke of Monmouth, illegitimate son of Charles II was forced to hide at Toddington after being implicated in the Rye House Plot. He was exiled and Henrietta followed him, but returned to Toddington. Monmouth was executed in 1685 following the Battle of Sedgemoor and Henrietta died a year later. Sixty years later sees the manor in serious disrepair and partially dismantled by William Wentworth, the Earl of Strafford, the only parts remaining more or less intact being the North East Corner, the kitchens and one solitary turret.
In 1806, the ruin was bought by John Cooper Esq who, together with his son-in-law, William Dodge Cooper Cooper, set about restoring the manor to its former glory and this is how it stands today.
It is with John Cooper that our story begins…..

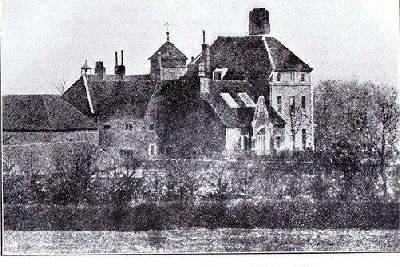
The Manor House, 1860
John Cooper Esq
Not too much is known of John Cooper and his early life other than that he was born on 16th January 1759 and baptised on February 11th. He married Jane Gidden – who was probably from Wilmslow, Cheshire – and they had one daughter, Elizabeth. John’s father, Thomas, appears to have changed the family name from Cowper to Cooper and of the twelve children he sired, only two, John and Sarah, survived infancy. Sarah also died quite young as well – in her late teens – as she passed away in 1785. John must have been the lucky one.
When he bought Toddington Manor in 1804, he had already amassed a lot of property as far flung as Ashley, Timperley, Partington and Hale in Cheshire, Rayleigh, Gravesend and Ramsgate in Kent as well as a house in Finsbury Square, London. Property in West Thurrock and two small farms in Bayhouse were purchased in 1807. This amounted to some 706 acres. Between 1806 and 1809, John Cooper purchased the Highgate brewery – a business which was known to exist in the 1670s – in Highgate, London from John Addison who had purchased it himself from the Southcote family not long before. It cost Cooper £1,000 pounds and comprised three parcels of land (£480 + £420 + £100) and probably included the brewery and yard. Under Addison, the brewing activities relocated to Homerton and John Cooper dismantled the brewery and turned the lands into his Town House Estate, Park House. The total area was approximately twelve and a half acres. A more detailed history of Park House is described in a later section.
John Cooper was Sheriff of Bedford in 1812.
His daughter, Elizabeth, married her cousin, William Dodge Cooper Heap in 1803 and it can only be assumed that this was ‘arranged’ in order to keep the manor – and all other property owned by John Cooper – safe within the family. Part of the provision of this marriage was that William change his surname to Cooper which he officially did in 1819.
John Cooper died in 1817 and his will published in October of that year named Elizabeth Cooper as his heir.
William Dodge Cooper Cooper
William Dodge Cooper Heap was born at South Hayling – on Hayling Island in Hampshire – to the Curate of South Hayling, Rev John Heap and Anne Dodge Cooper, who was born and brought up in Bosden, near Cheadle in Cheshire. A custom of the times was to include past family surnames in a young child’s forenames, thus when young William he was baptised with the names of his maternal great grandparents.
The life of a Churchman would often mean a lot of moving around, and so it was with the Heaps: The Rev John would take his family to Westborne in 1795.
On 19th March, 1803, in the County of Middlesex (at St Luke’s Church, Old Street, Finsbury), William married John Cooper’s daughter and heiress, Elizabeth.
Because she was his cousin, part of the marriage agreement was that he changed his surname to Cooper in order to inherit. This he did in the year of 1819 by Letters Patent following the death of his father-in-law.
William Dodge Cooper Cooper was now Lord of the Manor in Toddington and a leading landowner in Highgate. He appears to have divided the majority of his time between the two estates and rather than sit back and play the country squire, was extremely active in his duties. He was a magistrate in both Bedfordshire and Middlesex and was Deputy Lieutenant in the former as well as being Sheriff in 1824.
He chaired the Assembly at the Gatehouse Public House in Highgate and was Chairman/Treasurer of Highgate Public School as well being on the Management Committee of the National School – now St Michael’s – a short walk along North Road from the public school. Book Society Meetings were also held at Park House.
William and Elizabeth had several children: John was born on 30th January 1804 but probably died in infancy as no further records can be found; Jane, who was both deaf and dumb, on 7th November 1805; Elizabeth on 30th November 1806; William was born 10th April 1810; Amelia, 15th November 1812; Caroline on 4th September 1813; Henrietta on the 2nd September 1815, but sadly died at the age of 5 on 7th June 1821. Lucy followed 1st November 1818. Alfred John was born on 31st August 1819 but also did not survive infancy. James Lyndsay, 12th February 1821. Elizabeth married a Dutch count and Lucy was espoused to Henry (later Sir) Robinson of Knapton in Norfolk. Amelia’s marriage at the age of 36 was not so grand: Moses Tearle was a twenty one year old labourer, probably working for the Lord of The Manor at Toddington and one can only speculate on the circumstances of this liaison.
The stories of these three girls – Elizabeth, Lucy and Amelia – have been expertly told elsewhere, so I will not go into any significant detail here.
The London Gazette dated 12th February 1829 states that William and all other elected Sheriffs of their Counties were present at the King’s Court at Windsor – presumably for investiture by his majesty, King George IV.
There is a similar entry for 13th November 1827 and a notice of nomination on Nov 10th 1828. Commission signed by the Lord Lieutenant of the County of Bedford:
William Dodge Cooper Cooper, Esq. to be Deputy Lieutenant. Dated 27th March 1834.
William was very keen to encourage his labourers and was a leading light in allotting them small pieces of lands on his estate – allotments. In 1835, the secretary of Society for the Encouragement of Arts, George Atkin, wrote to the Lord of the Manor enquiring as to ‘how far the good results that followed the first introduction of this plan continue to be realized’. William replies – apologising for the delay as he was away from home (the letter was sent from Park House on the 5th of August, 1835) and assures Mr Atkin that he has made some observations which he trusts will not be unacceptable. In other words, we may gather that the scheme was a great success. The letter is signed as ‘Wm. D.C. Cooper’.
In 1839 it was noted that ‘William D.C. Cooper was the largest landowner in the parish with 706 acres’ – this would be his estates in West Thurrock and Bayhouse.
In the census of 1841, the family is living at Park House. Joining them is eldest son William’s wife, Laura (nee Ellis) and presumably their son William Smith Cowper Cooper who was born in 1832, the year after his parents were married. The house also boasts six household servants.
It was also noted in the Dover Telegraph of 1850 that William was ‘Present at Dinner’ on the 30th of November in Ramsgate, Kent. William had a house in Nelson’s Crescent, overlooking the harbour.
In 1851, a very long winded document states that, for the lands that William Dodge Cooper and his wife (as well as other landowners) owned in the parish of Harlington that had been leased to tenants under the Act of Enclosure, the price of a bushel of wheat need be determined in order that a fair tithe, rent or corn rent could be established for the previous 10 years, these dues being payable to the vicar of the parish church of Harlington.
In 1855, William presented the village with a water pump, sited on the village green. Sources inform me that this was still in use during World War II and it was quite hazardous to collect the water as the Luftwaffe were continually trying to bomb the nearby tank factory! It is probably that the pump replaced a pond in the square which would have provided for townspeople and also visitors and there livestock ie horses. In all likelihood, two people with a large bucket on a stick carried on their shoulders would be the method of obtaining water.
Elizabeth, daughter of John Cooper and wife of William, died on 6th June 1855 – she was 72. We can only imagine the grief in the household. The more so as their daughter Jane died the following year on the 9th August 1856.
On the 2nd of March 1856, one Samuel Fletcher was convicted for stealing two steel rabbit traps of the value of 7 shillings, which were the property of William D C Cooper Esq at Toddington. Fletcher was was sentenced to 1 month of hard labour. Poaching was clearly a problem – as we shall see later in the story of William D. C’s son, William.
William Dodge Cooper Cooper died on 9th August, 1860 at the age of 78.
William’s will was proven in Her Majesty’s (Queen Victoria) Court of Probate on 6th October 1860 naming William Cooper Cooper and the Rev James Lyndsay Cooper Cooper as executors. A notice appeared in the London Gazette dated 17th March 1865 and was published by N C and C Milne – the family solicitors.
Major William Cooper Cooper
William Cooper Cooper (he doesn’t seem to have any other names) became the Lord of the Manor on the death of his father. He was 50 years old. When he was 21, he married Laura Ellis – on 26th April 1831 – and a year later their only son, William Smith Cowper Cooper, was born. Laura was the daughter of Captain Thomas Ellis of Tuy-dee Park, Monmouthshire. He was a Justice of the Peace as well as Deputy Lieutenant of Cheltenham, Gloucestershire. Whilst perpetuating the use of family surnames (was Smith from Laura Ellis’ side?) it rather looks as though William the father was looking at the earlier spelling of their surname when naming his child.
Commissions signed by the Vice Lieutenant of the County of Bedford name William as vice Lieutenant from 1843, and 3 years later on the 21st February 1846, William (Gent) enlisted in the Bedfordshire Militia as a lieutenant. At some point he was promoted to Captain, for the London Gazette reports on the 24th March, 1858, Captain William Cooper Cooper ‘be a Major’. It is not known when, but William left the militia sometime after that. In 1855, the regiment was sent to Ireland from Aldershot for garrison duty during the Crimea war. The Militia had been reorganised in 1852 because of the threat of invasion from Napoleon III.
Still surviving is a water colour painting, shown below, of a view of his office in Aldershot…
…as well as this painting of a private of the Bedford Light Infantry Militia.
Clearly William had an artistic bent since he was known as a collector as well as being a pioneer in the art of photography. Here, below, we see a very early photograph taken by William, in 1854.
It was mentioned earlier about the nuisance of poachers. Well, the above photograph shows one caught by Norman Snoxall, the gamekeeper for the Toddington estate, who was a former police officer in another part of Bedfordshire. He died a couple of years after this photo was taken. What became of the poacher is unknown.
William’s apparent love of this artistic doesn’t just stop with painting and photography: some years earlier – 1836, when William’s father was alive – a Roman brooch was dug up by a gang of labourers and taken to William who, according to the story, promptly bought it. I have speculated elsewhere as to whether one William Tearle was amongst those labourers and even contemplated the possibility that he could have been the man who dug up the artifact. Probably, we shall never know.
Also in the William Cooper Cooper collection is the Toddington Brooch. An Anglo Saxon cruciform brooch, this has been dated to the 6th century and whilst it has been questioned as to whether it was found at Toddington, the describer (name and source unknown) points out that “Major Cooper Cooper is known to have collected material from Toddington”.
In 1844, William purchased at auction a carving entitled “Apollo and the Muses” – a piece that had previously been part of the old Manor House before its near destruction by the Earl Strafford. The myth of Apollo and the Muses is well known. The subject represents Apollo and the nine muses in concert, and is full of exquisite detail, the figures in high relief; The date is thought to be of the sixteenth century. It measures 6 feet by 4 feet two inches, and weighs about two hundredweight.
It might be suggested that the Cooper dynasty set about restoring the Manor – John and William Dodge with the structural building and William Dodge and son William concentrating on the more aesthetic aspect – for example, the grand fireplace:
William continued to photograph Toddington and it must be said that we have all benefited from his foresight. Some of these pictures are reproduced in the Miscellany section below.
On Feb 2nd 1867 William was present at the Queen’s Court on the Isle of Wight – Osborne House – for his investiture as Sheriff of the County of Bedfordshire.
William died in 1898 and his place as Lord of the Manor was taken by his son, William Smith Cowper Cooper.
And, sadly, here the story ends, for this William died a mere 7 years later in 1905. With no male heirs, the Manor house was sold as was the London residence, Park House.
William did have children, however – 4 girls:
Edith born 1860 – married Reginald William Borlase Warren Vernon,
Leila born 1862 died 1882 and appears on Caroline’s memorial,
Harriet born 1868 – married Lionel Tufnell,
Ida born 1870 died 1876.
All four girls had Cowper Cooper as their last two names and when the two surviving daughters married,that was the end of the Cooper surname.
The family were only residents at Toddington for a hundred years, but I like to think that their restoration of the building both inside and out and the way in which they conducted themselves as Lords of the Manor has left a legacy that has enriched the history of a little Bedfordshire village called Toddington.
Park House, Highgate
I have explained how John Cooper bought the land, sold the brewery that stood there and built his town house on the land. Here, exactly, is where it stood: the site of Park House and its grounds sits on a plateau of land in Highgate, a part of the Northern Heights of London, forming a triangle between Southwood Lane on the east side, North Hill to the west . On the northern side there is a steep bank known as The Bulwarks and Highgate Village is a five minute walk to the west. Beyond The Bulwarks, Highgate Wood – formerly The Bishop’s Wood – spreads towards Muswell Hill; Hampstead Heath is only a short walk to the west. In the days of the Cooper Coopers, and for very many years before, the surrounding land was used for rough grazing. Highgate is still is termed a Village today, but in those days it would certainly be more recognisable as such rather than a concrete extension of the crawling spider that is London now.
It is interesting to note that an unknown article dated 1851 refers to Park House being known as the residence of ‘Squire Cooper’, though whether this refers to William DCC – who would have been Squire at the time – or his father, John, is not stated. Either – or both – would often ride in the direction of Muswell Hill through Gravel Pit Wood (now Queen’s Woods) and my guess would be that the path would possibly take the course of Muswell Hill Road, which today separates the two forested areas. Whatever form it took, the ride was known as ‘Squire Cooper’s Ride’.
Wide and busy, the Archway Road, cuts off Highgate Woods from The Bulwarks; one can only imagine the true extent of uninterrupted scenery, with its sometimes gentle, sometimes steep undulations, deep forest and rough grazing land.
Not too many years ago, excavations very close to – and within the grounds of – Park House revealed not only cellars related to the brewery that had stood there, but also a series of tunnels. It would appear that these were made with intention of hiding Militia at a time when the threat of invasion from Napoleonic France was very real.
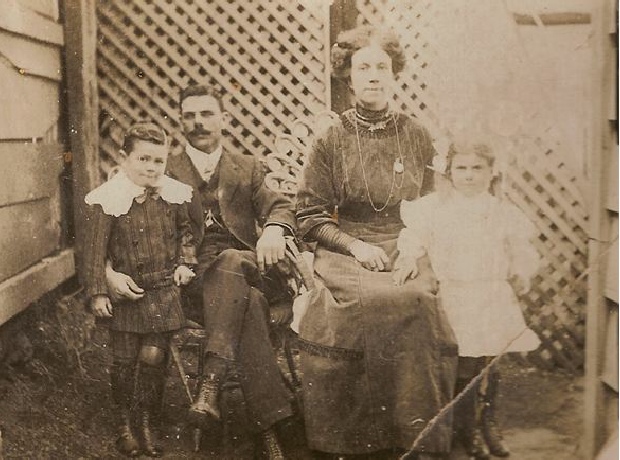
It is most likely, too, that my ancestor Moses Tearle – who married William DCC’s daughter Amelia – spent some time at Park House with the family; they were married in Hornsey.
The untimely and early death of William Smith Cowper Cooper meant the end of Park House – as it did of Toddington Manor – and the Highgate residence was sold.
In 1848 it had been converted from a school for backward children into a refuge for prostitutes and in 1855 it was leased to the London Diocesan Penitentiary (later the House of Mercy) for, it would seem, the same purpose. The poet Christina Rosetti was a volunteer here. In 1900 it passed to the Clewer sisters but fell vacant in 1940.
The House survived for another 7 years before it was demolished to make way for the estate built by Hornsey Borough Council for the main purpose of housing those who had lost their homes during the war and new, young families. It was aptly named Hillcrest and still survives today, though many of the apartments are privately owned.
The seven blocks of flats were all named after leading military men of the second world war – Tedder, Dowding, Montgomory, Mountbatten, Cunningham, Alexander and Wavell. And it was into No 6, Wavell House that Leslie and Mollie Tearle, with their two young children Barbara and myself, Richard, moved in the year of 1949. It would be almost 50 years before this amazing coincidence of family history would be discovered.

The actual site of Park House is unknown and although this view and that of Wavell House (below) do look similar, I don’t believe that they are compatible. The Hornsey Society article states that Park House faces North Hill and is located fairly centrally. If this is the case, it would have been a little behind and to the right of where the photographer was standing to take the picture of Wavell House.

Entrance to the Hillcrest Estate in Southwood Lane. Park House Passage is on the left and leads to North Hill and the Wrestlers Public House.

“The Bulwarks” from the junction of Park Road and Southwood Lane. The visible block of flats is the rear of Wavell House.
Miscellany
In writing this story there have been many ‘tangents’ which I have reluctantly ignored in the main body of the text as well as numerous photographs which, though of high relevance, might have distracted from the story. I hope to put some of that right in this section, though things will not be in any chronological order nor any particular order of priority.
(Major William Cooper Cooper was known to have been the photographer for pictures 1,3 and 4 – perhaps others).
Brief mention has been made of other children of William Dodge Cooper Cooper and it is worth adding just a little more. Lucy married Henry Robinson of Knapton in Norfolk on 14th July 1842 and bore him five children. In 1845 he was knighted, but it transpires that he had a mistress and sired three children on her. The marriage continued, but one wonders about the situation and what grief Lucy must have endured. She died in 1889 aged 71 and her memorial appears with her husband’s in Knapton Church.
Elizabeth married a Dutch nobleman, Count Alexander Charles Joseph Vander Burch, chamberlain to His Majesty the King of the Netherlands. Much of her time would have been spent abroad, but there is evidence to suggest that she made visits to her sisters in Toddington.
Amelia’s marriage to Moses Tearle has never been recorded in any official records and their story is one of the most intriguing. Moses changed his name to Cecil (Cecill in some accounts) but no one has yet discovered the reason why! They moved away from the area and Wendy Skelley has given us an excellent account of the lives of their sons. See other articles on Egerton and Aubrey
Caroline Cooper Cooper lived at Toddington all her life, never marrying, and died at the age of 88 in 1901.
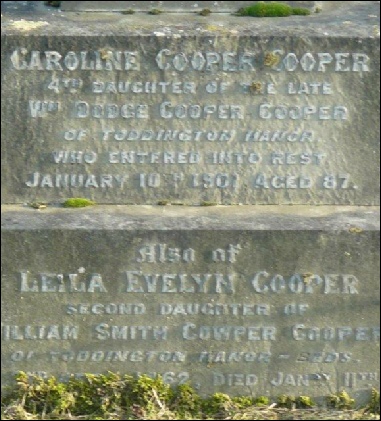
Caroline’s grave in Toddington Cemetery together with Leila Evelyn, daughter of William Smith Cowper Cooper.

Caroline’s grave in Toddington Cemetery together with Leila Evelyn, daughter of William Smith Cowper Cooper.

Still in existence is a cookery book signed on the front page by Caroline – that its recipes are for foreign food suggests that it may have been given to her by her sister, Elizabeth. It is dated 1848 in her hand.

The South Window – “Faith Hope and Charity” donated by Caroline Cooper Cooper in memory of her parents
A window in Toddington Church was donated by Caroline.
Circa 1892, she wrote: “I have promised my brother Major Cooper that I will contribute whatever he may require up to £150 for the window now being erected in Toddington Church in memory of my late father and mother. If this is not paid before my death it will of course be a debt due on my Estate which I desire you to satisfy.
If the stained glass window is not paid for before my death £250 more or less to be paid for it – in memory of my dear father and mother.
The South Window – “Faith Hope and Charity” donated by Caroline Cooper Cooper in memory of her parents
James Lindsay Cooper Cooper was the youngest of the family and entered the Church quite early in his life. As patron of the Living of Toddington, his father presented him to the people in 1846 when he was aged 25. A year earlier, James had married Rebecca Singleton and their only child, also named Rebecca, died at just six months of age.
James resigned from the Church on inheriting property in 1862, but a mere 8 years later he, too, died at the young age of 48. A six and half hundredweight bell (no 2 at Toddington Church) and made by John Warner was inscribed in 1906: “To the glory of God and in memory of the Rev James Lindsay Cooper Cooper by his widow.”
“In addition to archaeological work carried out by professional archaeology units, some useful work was done by Victorian antiquaries. Major C Cooper of Toddington Manor published several reports of finds from the Toddington district. Two early Anglo-Saxon brooches, believed found in the 19th century by Major Cooper in Toddington parish (exact provenance unknown), are in the collections of Northampton Museum. One of these, a large cruciform brooch, is the subject of a detailed analysis by Kennet (1969).”
You can download the PDF from the list in the link to Kennet. The title is: A late 6th-century cruciform brooch from Toddington, Bedfordshire: an Anglo-Saxon connexion examined (pp 206-9)
Kennett, David H
I had hoped to include illustrations of this cruciform brooch as well as the ‘famous’ bronze elephant found on Major Cooper’s land, but the only ones I have found are in PDF format and cannot be reproduced here.

Notes by “Adams” on the works carried out by William D. C. Cooper and of the Apollo carving bought by his son, Major Cooper Cooper
Sources, thanks and acknowledgements
In writing this account, I have borrowed from the stories of the Toddington Tearles excellently written by Barbara Tearle and Ewart Tearle and I have tried to knit these tales together without diverting attention away from them. Likewise from Wendy Skelley in New Zealand who with great kindness sent me just about all her research notes, so the hard work was hers and any mistakes have been my misinterpretations or conclusion jumping. It was her enthusiasm for the project when I first suggested that I attempt it that spurred me on. Thank you all.
Various publications have been used to gain some further snippets of information: The London Gazette (online), Bedfordshire at War, and numerous books on Bedfordshire. Also to Hornsey Historical Society for an article on Park house which I have used to base my narrative of that section. The picture of Park House also comes from that source.
Mention must be made of the Toddington Village page on Facebook and especially Phil Mead whose clear love of the village has led him to find out so much that has to do with the Cooper Coopers. He – and one or two others there – have answered my often stupid questions and also provided very valuable information that may not have been obtainable elsewhere. And it is them that I must thank, too, for so many of the illustrations of Toddington Manor and the general area.
Richard Tearle
February 2012